Arterial ulcers are a severe type of wound caused by poor blood circulation due to blocked arteries. These ulcers primarily develop on the lower extremities, especially on the feet and toes. If left untreated, they can lead to serious complications, including infection and tissue necrosis. In this blog, we will explore arterial ulcer causes, symptoms, and treatment options, along with prevention strategies to maintain optimal vascular health.
What Are Arterial Ulcers?
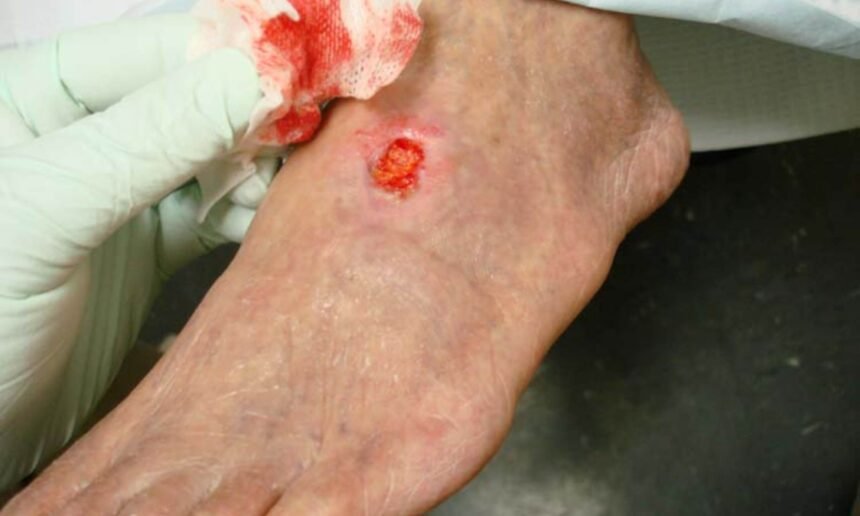
Arterial ulcers, also known as ischemic ulcers, result from peripheral artery disease (PAD), where reduced blood flow prevents proper wound healing. These ulcers are often painful and have well-defined edges with a pale or necrotic wound bed.
Causes of Arterial Ulcers
The primary cause of arterial ulcers is poor blood circulation due to arterial blockages. Several underlying conditions contribute to their development, including:
- Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) – Narrowing of arteries reduces blood supply to the limbs.
- Atherosclerosis – Fatty plaque buildup in arteries restricts blood flow.
- Diabetes – High blood sugar levels damage blood vessels, leading to circulation problems.
- Smoking – Increases arterial constriction and reduces oxygen supply to tissues.
- Hypertension (High Blood Pressure) – Puts stress on artery walls, worsening circulation issues.
- Obesity – Leads to vascular inflammation and impaired circulation.
These risk factors not only contribute to ulcer formation but also delay healing if not managed early. You can explore a more detailed explanation of the key risk factors for developing arterial ulcers along with prevention strategies in our dedicated guide.
Symptoms of Arterial Ulcers
Recognizing the early signs of arterial ulcers can help in timely medical intervention. Common symptoms include:
- Deep, punched-out wound appearance with sharply defined edges.
- Pain that worsens at night or when the leg is elevated.
- Pale, dry, or necrotic wound bed with little to no bleeding.
- Cold or shiny skin around the ulcer due to poor circulation.
- Delayed wound healing and risk of infection.
- Reduced or absent pulses in the affected limb.
Treatment Options for Arterial Ulcers
Effective treatment for arterial ulcers focuses on improving blood flow, wound care, and preventing infections. Treatment options include:
1. Medical Interventions
- Revascularization procedures: Angioplasty or bypass surgery can restore blood flow to the affected area.
- Medications: Blood thinners, cholesterol-lowering drugs, and antihypertensive medications help improve circulation.
- Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT): Enhances oxygen supply to promote healing.
2. Wound Care Management
- Debridement: Removal of dead tissue to promote healing.
- Specialized dressings: Hydrocolloid or foam dressings keep wounds moist and protected.
- Antibiotics: Used to treat infections if present.
- Offloading pressure: Using protective footwear or orthotics to reduce pressure on the ulcer.
3. Lifestyle Changes for Prevention
- Quit smoking to improve vascular health.
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in fiber, lean proteins, and healthy fats to reduce cholesterol levels.
- Exercise regularly to enhance circulation and promote overall health.
- Monitor blood sugar levels if you have diabetes to prevent further complications.
- Proper foot care: Regularly inspect feet for cuts, ulcers, or changes in skin color.
Conclusion
Arterial ulcers are a serious medical condition that requires immediate attention. Understanding their causes, symptoms, and treatment options can help prevent complications and promote better healing. If you or a loved one experience symptoms of an arterial ulcer, consult a healthcare professional promptly to prevent further complications. Timely recognition and proper care are essential for managing arterial ulcers. If you’re unsure whether the wound is arterial or something else, understanding the difference between arterial and venous ulcers can help guide the right treatment.

Leave a Reply