An infectious wound is a type of wound that becomes contaminated with bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites, leading to delayed healing and potential complications. Infections can arise from minor cuts, surgical wounds, burns, or chronic ulcers if not properly treated. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for preventing severe complications like sepsis or gangrene.
Causes of Infectious Wounds
Wounds become infected when harmful microorganisms enter the body through broken skin. Several factors contribute to wound infections, including:
1. Bacterial Infection
- Staphylococcus aureus (including MRSA) and Streptococcus are common culprits.
- Occurs when bacteria enter an open wound due to poor hygiene or contaminated surfaces.
2. Viral Infection
- Some viral infections, like herpes simplex, can cause wound infections.
- Can develop due to compromised immunity or direct contact with infected fluids.
3. Fungal Infection
- Wounds in moist areas or people with weakened immune systems are prone to fungal infections.
- Candida and Aspergillus are common fungi affecting wounds.
4. Poor Wound Care
- Failure to clean and cover wounds properly increases the risk of infection.
- Using dirty bandages or touching wounds with unclean hands introduces bacteria.
5. Underlying Health Conditions
- People with diabetes, poor circulation, or a weak immune system are at higher risk.
- Conditions like chronic venous insufficiency and pressure ulcers increase susceptibility.
- People with chronic wounds are more prone to infections. Learn more about the link between long-term wounds and infections in our post on Chronic Wounds and Infection Risk.
Symptoms of an Infected Wound
Recognizing early symptoms of wound infections is vital for preventing complications. Common signs include:
- Increased Redness & Swelling – The wound and surrounding skin become inflamed.
- Warmth & Tenderness – The infected area may feel hot and painful to touch.
- Pus or Foul-Smelling Discharge – Thick, yellow, green, or bloody drainage indicates infection.
- Fever & Chills – Systemic infection may lead to elevated body temperature.
- Delayed Healing – If a wound does not heal within two weeks, infection might be the cause.
- Black or Necrotic Tissue – Indicates severe infection and possible tissue death.
Treatment Options for Infectious Wounds
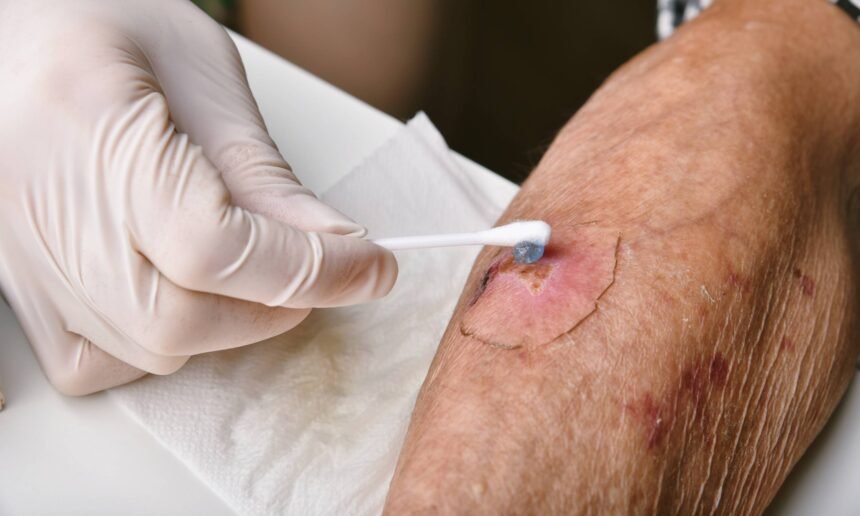
1. Wound Cleaning & Disinfection
- Clean the wound daily with saline solution or mild antiseptics.
- Avoid harsh chemicals like hydrogen peroxide, as they can damage healthy tissue.
For step-by-step wound cleaning and dressing instructions you can follow at home, read our guide on How to Clean and Care for an Infected Wound at Home.
2. Antibiotics & Medications
- Topical antibiotics (like Neosporin or mupirocin) for mild infections.
- Oral or IV antibiotics for severe bacterial infections.
- Antifungal creams or oral medications for fungal infections.
3. Proper Wound Dressing
- Use moist wound dressings (hydrocolloid, foam, or antimicrobial dressings) to promote healing.
- Change dressings regularly to prevent reinfection.
4. Debridement (Removing Dead Tissue)
- Surgical, enzymatic, or mechanical debridement removes necrotic tissue and promotes healing.
- Required for severe infections or chronic wounds.
5. Advanced Wound Care Therapies
- Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT): Uses suction to remove bacteria and fluids.
- Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT): Helps infected wounds heal faster by increasing oxygen supply.
6. Managing Underlying Health Conditions
- Control blood sugar levels if diabetic to prevent recurrent infections.
- Improve blood circulation by staying active and maintaining a healthy diet.
Prevention of Infectious Wounds
Following proper wound care practices helps prevent infections and complications:
- Wash hands thoroughly before touching wounds.
- Keep wounds covered with clean, sterile dressings.
- Change bandages daily or when soiled.
- Avoid scratching or picking at scabs.
- Boost immunity with a healthy diet and hydration.
- Seek medical help if a wound shows signs of infection.
Conclusion
Infectious wounds can lead to serious health complications if not treated properly. By understanding the causes, recognizing symptoms early, and following proper wound care and treatment, you can prevent infections and promote faster healing. If a wound shows signs of infection, seek medical attention immediately to avoid severe outcomes.

Leave a Reply